- Home
- Cancer Prevention
- Sun protection
- Understanding UV radiation
- How UV radiation increases skin cancer risk
How UV radiation increases skin cancer risk
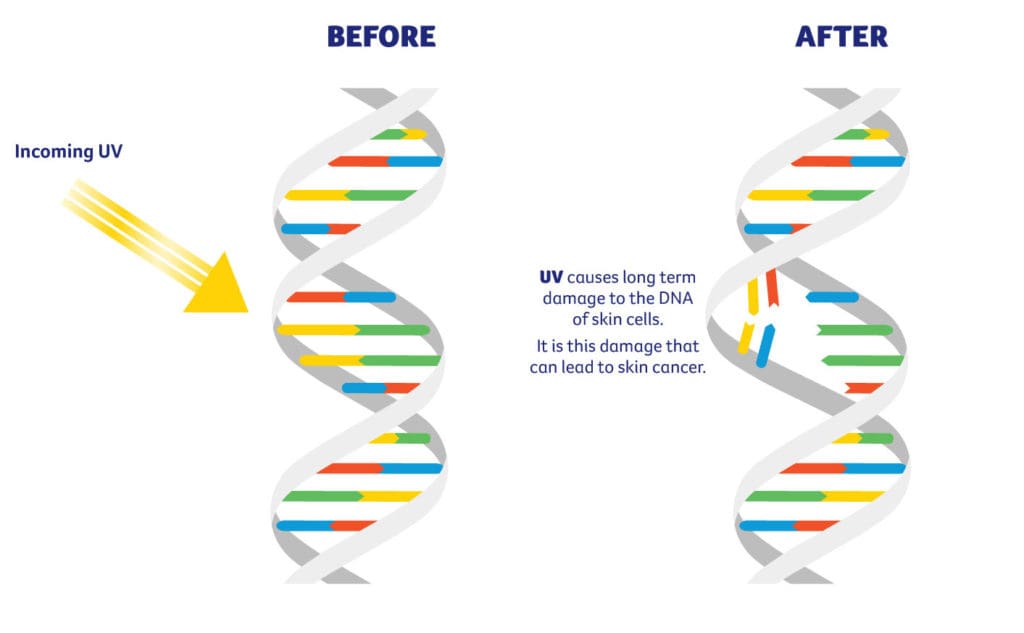
When your skin is unprotected from the sun, ultraviolet (UV) radiation can damage your DNA. If the body is unable to repair this damage the cell can begin to divide and grow in an uncontrolled way. This growth can eventually form a tumour.
UV radiation is made up of UVA and UVB rays which can penetrate the skin and cause permanent damage, contributing to melanoma and other skin cancers, sunburn, skin ageing and eye damage:
- UVA penetrates deeply into the skin (the dermis) causing genetic damage to cells, photo-ageing (wrinkling, blotchiness etc) and immune-suppression.
- UVB penetrates the top layer of the skin (the epidermis) causing damage to the cells. UVB is responsible for sunburn – a significant risk factor for skin cancer, especially melanoma.
Get to know your skin and consult your doctor if you notice any changes or new spots.
It’s also important to remember that damage is not always visible, damage starts long before a sunburn or tan occurs, and is permanent and cumulative; much of the DNA damage to skin cells is impossible to repair by our body.
The good news is it’s never too late to reduce your risk. Learn the five ways you can protect yourself.
