- Home
- Cancer Prevention
- Smoking
- Smoking in NSW
Smoking in NSW
Tobacco is the greatest preventable cause of cancer with 1 in 8 cancer cases and 1 in 5 cancer deaths caused by smoking. Lung cancer remains the largest cause of death in Australia, with about 81% of lung cancer cases estimated to be as a result of tobacco smoking.
In 2019, 15.5% of NSW adults were current smokers. While there has been a long-term reduction in smoking, since 2015, daily smoking rates have remained relatively unchanged. Aboriginal people are almost 3 times more likely to smoke compared to non-Indigenous Australians.
The prevalence of smoking is significantly higher among disadvantaged groups making smoking an important social justice issue. Smoking damages people’s health, increases their financial stress, contributes to cycles of poverty and erodes their quality of life.
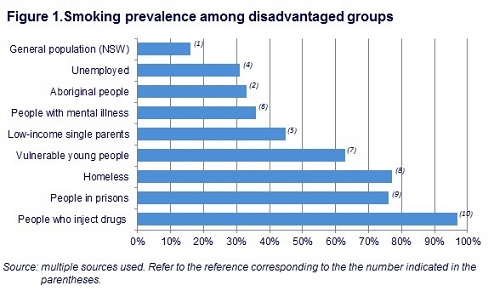
For more information on the prevalence of smoking in NSW, go to the Tobacco in Australia website.
Does smoking cause cancer?
Cigarette smoke contains more than 7,000 chemicals including 69 that are carcinogens (known to cause cancer). When you inhale, these chemicals enter your lungs and spread through your body via blood and lymph systems. This can interrupt normal cell growth, causing cells to multiply too fast or develop abnormally, which can (and often does) result in cancer cells.
Exposure to second-hand smoke is a cause of lung cancer in non-smokers. When smokers expose non-smokers to second-hand smoke, they inhale many of the same cancer-causing chemicals that smokers inhale.
For more information on smoking and cancer, go to the Tobacco in Australia website.
Are smoking rates declining?
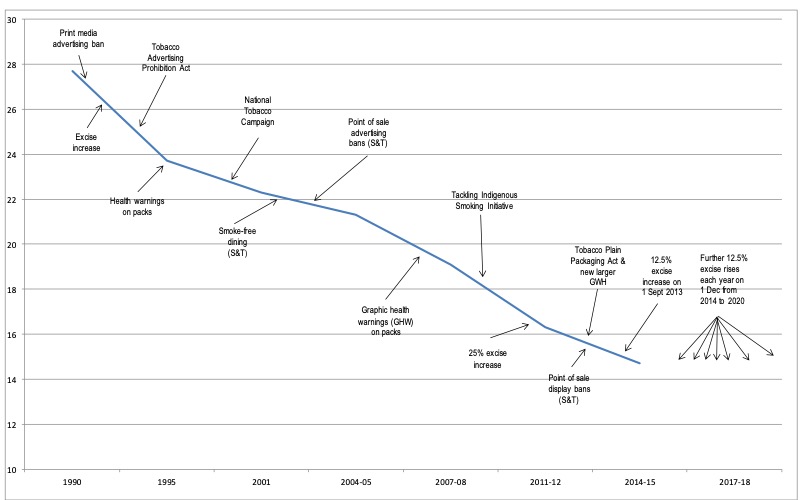
The adult smoking rate has been declining since the mid 1970’s. This decline is likely to be a result of sustained government tobacco control strategies such as raising tobacco taxes, advertising bans, mass media public education campaigns and comprehensive smoke-free environments legislation.
The following graph shows the smoking prevalence for daily smokers aged 18 years or older against key tobacco control measures implemented in Australia since 1990.